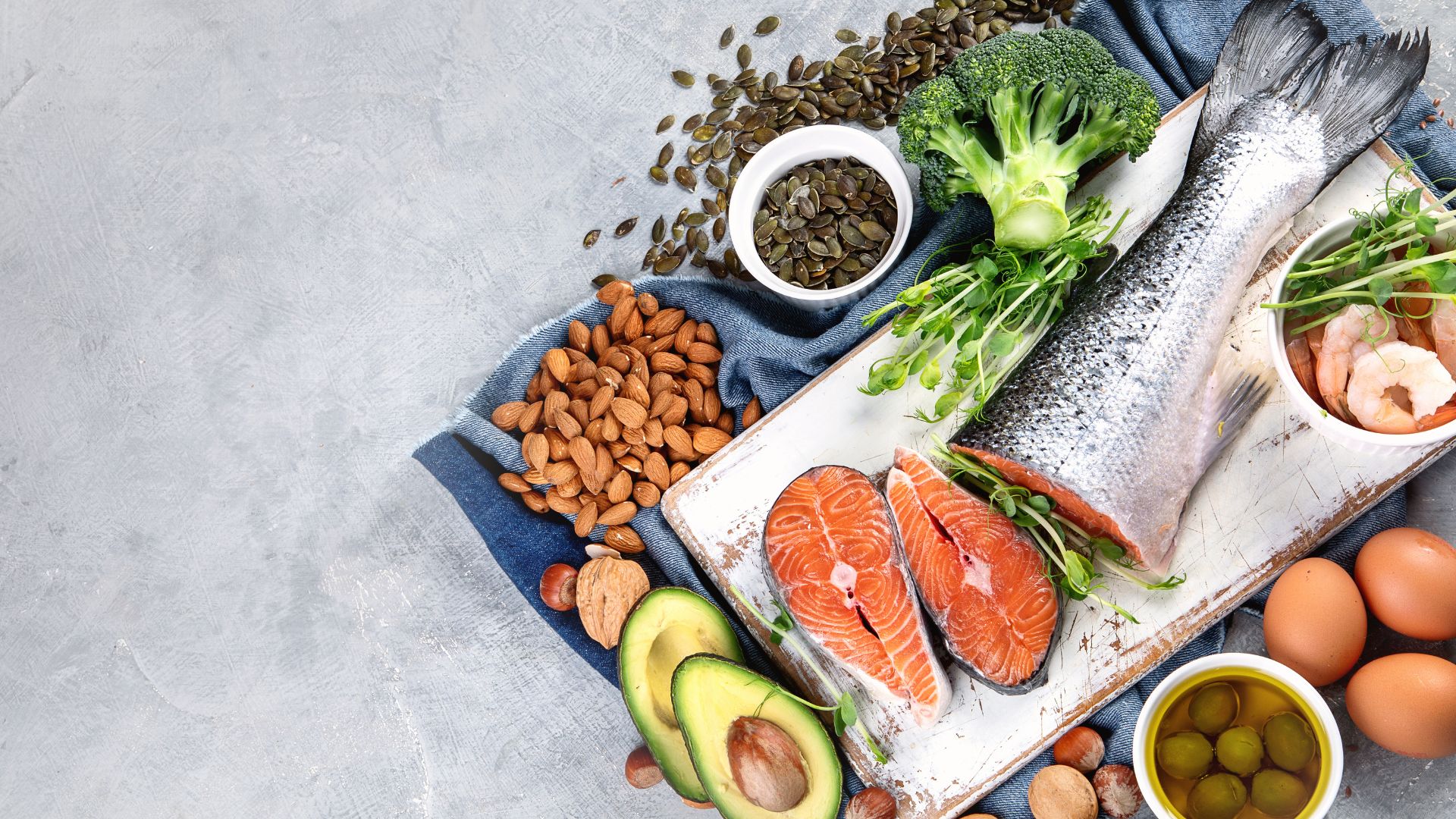
Fatty acids are an essential component of a healthy diet, providing many significant benefits for the body. Found in foods like nuts, fish, and olive oil, fatty acids can be divided into two main categories: saturated and unsaturated.
Saturated fatty acids are typically solid at room temperature and come from animal sources such as meat, eggs, butter, and cheese.
Unsaturated fats are generally liquid at room temperature and come from plant-based sources such as nuts, avocados, and seeds. Both types of fatty acids have been linked to reducing inflammation in the body, which is associated with many chronic diseases.
Fatty acids provide energy for cells to perform their functions and help transport vitamins A, D, E & K throughout the body. They also help form cell membranes by regulating fluidity and permeability within cells.
Structure

The structure is key to understanding fatty acids and their role in our health. Fatty acids are molecules composed of carbon-hydrogen bonds that make up some of our cells’ essential components and provide us with energy from food sources. They come in many forms, some necessary for life, while others can be toxic when consumed in large amounts. Understanding the structure and organization of these molecules is crucial for comprehending their use within our bodies.
Fatty acids play an essential role in cell membrane formation and energy production. Their molecular structure allows them to form various shapes, allowing them to interact with other molecules, such as proteins or carbohydrates. This allows fatty acids to act as a storehouse for energy by forming triglycerides used during fasting or exercise, helping give us the power we need throughout our day-to-day activities.
Health Benefits

Fatty acids are essential to human health and significantly affect our overall well-being. Our bodies can’t make fatty acids on their own, so we must get these compounds from the food we eat. Eating foods rich in fatty acids can positively affect our health, such as reducing inflammation, maintaining mental clarity, and keeping cholesterol levels low.
This article will discuss what fatty acids do and how they benefit us nutritionally. We’ll learn about the different types of fatty acids and how they interact with our bodies to boost our energy levels and improve overall health. We’ll also discuss which foods contain valuable rich acid sources so that you know which ones to add to your diet for maximum benefit. Finally, we’ll talk about ways to ensure you’re getting enough of the right kinds of fats for optimal health benefits.
Sources

Fatty acids are an important part of a healthy diet and lifestyle. They are essential for providing energy, building cells and hormones, and helping the body absorb fat-soluble vitamins. Knowing where to find fatty acids is key to gaining their benefits and avoiding potential health risks.
When getting enough fatty acids in your diet, it’s important to remember that not all sources are created equal. Animal sources like meat, dairy products, eggs, fish, and poultry contain saturated fats which can increase cholesterol levels if consumed in excess. Plant-based foods such as nuts and seeds provide healthier unsaturated fats like monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) or polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). These types of fats can help reduce bad cholesterol levels while maintaining good cholesterol levels.
Deficiencies
Fatty acids are essential for human health, but deficiencies can cause serious problems. This article examines what fatty acids do and how to identify if you have a fatty acid deficiency.
Most people don’t think about their fatty acid levels until something goes wrong. Yet, the body needs them for critical biological processes like cell growth and development and normal brain functioning. Essential fatty acids are those that we must obtain through our diet since the body cannot produce them on its own. Suppose there is an insufficient intake of these fats. In that case, it can lead to various symptoms, such as dry skin, fatigue, poor concentration or memory loss, digestive issues, and even depression.
The most common fatty acid deficiencies are omega-3s (found in fish oils) and linoleic acid (found in vegetable oils).
Risks

Fatty acids are an essential part of a healthy diet and offer many health benefits, but some risks are also associated with them. Overeating fatty acids can lead to weight gain, which increases the risk of severe illnesses such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. These fatty acids can also improve cholesterol levels in the body, which can cause blood vessels to become clogged, raising the risk for high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Additionally, not all types of fatty acids are good for you; saturated fats and trans-fats should be avoided because they have been linked to increased cholesterol levels in the body.
It’s important to consume fatty acids in moderation as part of a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It’s recommended that no more than 10 percent of your daily caloric intake come from fat sources.
Conclusion

Fatty acids are an essential part of human nutrition. They provide energy, aid in the functioning of organs and cells, and help create hormones. Understanding what fatty acids do is important for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and diet.
In conclusion, fatty acids are incredibly beneficial to our bodies. They provide energy and help form cell walls, create hormones, and aid in organ function. Including foods with healthy fats in your diet, such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, or seeds, is recommended. Additionally, avoiding processed foods or those high in trans fats can help maintain well-being. Taking time to understand what fatty acids do will allow you to make educated decisions regarding food choices that benefit your body and mind.
